![[商品価格に関しましては、リンクが作成された時点と現時点で情報が変更されている場合がございます。] [商品価格に関しましては、リンクが作成された時点と現時点で情報が変更されている場合がございます。]](https://hbb.afl.rakuten.co.jp/hgb/38aa1d8c.e4eba394.38aa1d8d.6467c674/?me_id=1213310&item_id=20853972&pc=https%3A%2F%2Fthumbnail.image.rakuten.co.jp%2F%400_mall%2Fbook%2Fcabinet%2F3603%2F9784297133603_1_2.jpg%3F_ex%3D128x128&s=128x128&t=picttext)
|
ゲームで学ぶ探索アルゴリズム実践入門〜木探索とメタヒューリスティクス [ 青木 栄太 ] |
|
|
 Edax の評価関数はこちら†に詳しい解説があるが、基本的には
Logistello† のそれを引き継いでおり、盤面を複数のパターンに分解し、それぞれのパターンに対し、多数の棋譜を元に事前にロジスティック回帰で求めておいた評価値表を引いて、その総和を評価値としている。
Edax の評価関数はこちら†に詳しい解説があるが、基本的には
Logistello† のそれを引き継いでおり、盤面を複数のパターンに分解し、それぞれのパターンに対し、多数の棋譜を元に事前にロジスティック回帰で求めておいた評価値表を引いて、その総和を評価値としている。
/** number of (unpacked) weights */
static const int EVAL_N_WEIGHT = 226315;
/** number of plies */
static const int EVAL_N_PLY = 61;
/** eval weights */
short ***EVAL_WEIGHT;
// allocation
EVAL_WEIGHT = (short***) malloc(2 * sizeof (*EVAL_WEIGHT));
if (EVAL_WEIGHT == NULL) fatal_error("Cannot evaluation weights.\n");
EVAL_WEIGHT[0] = (short**) malloc(2 * EVAL_N_PLY * sizeof (**EVAL_WEIGHT));
if (EVAL_WEIGHT[0] == NULL) fatal_error("Cannot evaluation weights.\n");
EVAL_WEIGHT[1] = EVAL_WEIGHT[0] + EVAL_N_PLY;
EVAL_WEIGHT[0][0] = (short*) malloc(2 * EVAL_N_PLY * EVAL_N_WEIGHT * sizeof (***EVAL_WEIGHT));
if (EVAL_WEIGHT[0][0] == NULL) fatal_error("Cannot evaluation weights.\n");
EVAL_WEIGHT[1][0] = EVAL_WEIGHT[0][0] + EVAL_N_PLY * EVAL_N_WEIGHT;
for (ply = 1; ply < EVAL_N_PLY; ply++) {
EVAL_WEIGHT[0][ply] = EVAL_WEIGHT[0][ply - 1] + EVAL_N_WEIGHT;
EVAL_WEIGHT[1][ply] = EVAL_WEIGHT[1][ply - 1] + EVAL_N_WEIGHT;
}
オリジナルのコードで表の実体をアロケートしているのは 16 行の EVAL_WEIGHT[0][0] で、55MB の巨大な配列になっている。
各パターンの配列は各桁が白、黒、空きに対応する3進数をインデックスにして参照される。
評価値を求める際には 46 要素のインデックスを用いて表を引くことになるが、このインデックスの生成は処理が重いため、
盤面に対応するインデックスの配列 eval feature を保持していて、盤面の更新と同期して変化したマスの分を更新している。
score = w[f[ 0]] + w[f[ 1]] + w[f[ 2]] + w[f[ 3]] + w[f[ 4]] + w[f[ 5]] + w[f[ 6]] + w[f[ 7]] + w[f[ 8]] + w[f[ 9]] + w[f[10]] + w[f[11]] + w[f[12]] + w[f[13]] + w[f[14]] + w[f[15]] + w[f[16]] + w[f[17]] + w[f[18]] + w[f[19]] + w[f[20]] + w[f[21]] + w[f[22]] + w[f[23]] + w[f[24]] + w[f[25]] + w[f[26]] + w[f[27]] + w[f[28]] + w[f[29]] + w[f[30]] + w[f[31]] + w[f[32]] + w[f[33]] + w[f[34]] + w[f[35]] + w[f[36]] + w[f[37]] + w[f[38]] + w[f[39]] + w[f[40]] + w[f[41]] + w[f[42]] + w[f[43]] + w[f[44]] + w[f[45]] + w[f[46]];各 ply ( = 60 - n_empties) に対する Eval weight は 226315 個の short の配列で宣言されているが、その中身は前述の評価パターン 12 種類に対する評価値表である。 構造体にした方が見やすいし、各要素のインデックスが 16ビットに納まるようになる(後述のベクター化の際に重要)。 (4.5.0)
typedef struct Eval_weight {
short C9[19683];
short C10[59049];
short S10[2][59049];
short S8[4][6561];
short S7[2187];
short S6[729];
short S5[243];
short S4[81];
short S0;
} Eval_weight;
Eval_weight (*EVAL_WEIGHT)[2][EVAL_N_PLY];
// allocation
EVAL_WEIGHT = (Eval_weight(*)[2][EVAL_N_PLY]) malloc(sizeof(*EVAL_WEIGHT));
if (EVAL_WEIGHT == NULL) fatal_error("Cannot allocate evaluation weights.\n");
return w->C9[f[ 0]] + w->C9[f[ 1]] + w->C9[f[ 2]] + w->C9[f[ 3]] + w->C10[f[ 4]] + w->C10[f[ 5]] + w->C10[f[ 6]] + w->C10[f[ 7]] + w->S10[0][f[ 8]] + w->S10[0][f[ 9]] + w->S10[0][f[10]] + w->S10[0][f[11]] + w->S10[1][f[12]] + w->S10[1][f[13]] + w->S10[1][f[14]] + w->S10[1][f[15]] + w->S8[0][f[16]] + w->S8[0][f[17]] + w->S8[0][f[18]] + w->S8[0][f[19]] + w->S8[1][f[20]] + w->S8[1][f[21]] + w->S8[1][f[22]] + w->S8[1][f[23]] + w->S8[2][f[24]] + w->S8[2][f[25]] + w->S8[2][f[26]] + w->S8[2][f[27]] + w->S8[3][f[28]] + w->S8[3][f[29]] + w->S7[f[30]] + w->S7[f[31]] + w->S7[f[32]] + w->S7[f[33]] + w->S6[f[34]] + w->S6[f[35]] + w->S6[f[36]] + w->S6[f[37]] + w->S5[f[38]] + w->S5[f[39]] + w->S5[f[40]] + w->S5[f[41]] + w->S4[f[42]] + w->S4[f[43]] + w->S4[f[44]] + w->S4[f[45]] + w->S0;
この使われる方の表(手番側から見た評価)だけを残すとメモリーを半減することができ、27.5MB の節約になる。 パスの時には eval feature の3進数の各桁を入れ替える必要があるが、パスの頻度は少ないし、 これも表引きで行えば(表は各パターン共通に使えるし、既に初期化の際にも使用している)、パスの時だけならそれほど重い処理でもない。 (4.4.7)
さらには 60・59 か所空きの評価値は実質一通りで意味がなく、58・57 か所空きの表で代用して全く問題ない。
また 10 か所空き以降はほぼ完全読みになり評価値はほとんど使われることがなく、12・11 か所空きの表で代用しても強さや速度に影響しない。これで計 4.5MB 節減できる。
評価値表の初期化は起動時の一回のみだがその実行時間は無視できず、表の削減は高速化にもなる。
const CoordinateToFeature *s = EVAL_X2F + move->x;
switch (s->n_feature) {
default:
feature[s->feature[6].i] -= 2 * s->feature[6].x; // FALLTHRU
case 6: feature[s->feature[5].i] -= 2 * s->feature[5].x; // FALLTHRU
case 5: feature[s->feature[4].i] -= 2 * s->feature[4].x; // FALLTHRU
case 4: feature[s->feature[3].i] -= 2 * s->feature[3].x;
feature[s->feature[2].i] -= 2 * s->feature[2].x;
feature[s->feature[1].i] -= 2 * s->feature[1].x;
feature[s->feature[0].i] -= 2 * s->feature[0].x;
break;
}
foreach_bit (x, f) {
s = EVAL_X2F + x;
switch (s->n_feature) {
default:
feature[s->feature[6].i] -= s->feature[6].x; // FALLTHRU
case 6: feature[s->feature[5].i] -= s->feature[5].x; // FALLTHRU
case 5: feature[s->feature[4].i] -= s->feature[4].x; // FALLTHRU
case 4: feature[s->feature[3].i] -= s->feature[3].x;
feature[s->feature[2].i] -= s->feature[2].x;
feature[s->feature[1].i] -= s->feature[1].x;
feature[s->feature[0].i] -= s->feature[0].x;
break;
}
}
AVX2 では一度に 16 ワードの 16 ビット変数を更新できるので、46 の eval feature をすべて更新するのに3命令しかかからない。
場合分けも不要だし、計算途中の 46 の eval feature はレジスターに保持できる。
ついでに(後述の、eval feature を復元するために保存する代わりに)更新後の eval feature を別変数に保存することも同コストでできる。 (4.4.5)
typedef union {
unsigned short us[48];
unsigned long long ull[12]; // SWAR
__m128i v8[6];
__m256i v16[3];
} EVAL_FEATURE_V;
__m256i f0 = _mm256_sub_epi16(eval_in->feature.v16[0], _mm256_slli_epi16(EVAL_FEATURE[x].v16[0], 1));
__m256i f1 = _mm256_sub_epi16(eval_in->feature.v16[1], _mm256_slli_epi16(EVAL_FEATURE[x].v16[1], 1));
__m256i f2 = _mm256_sub_epi16(eval_in->feature.v16[2], _mm256_slli_epi16(EVAL_FEATURE[x].v16[2], 1));
foreach_bit(x, f) {
f0 = _mm256_sub_epi16(f0, EVAL_FEATURE[x].v16[0]);
f1 = _mm256_sub_epi16(f1, EVAL_FEATURE[x].v16[1]);
f2 = _mm256_sub_epi16(f2, EVAL_FEATURE[x].v16[2]);
}
eval_out->feature.v16[0] = f0;
eval_out->feature.v16[1] = f1;
eval_out->feature.v16[2] = f2;
オリジナルでは盤面を戻すときにはアップデートと逆の操作を行っているが、打つ前の eval feature を保存しておき、それに戻す方が速い。 (4.4.6)
typedef struct Eval_weight {
short S0; // also acts as guard for VGATHERDD access
short C9[19683];
short C10[59049];
short S100[59049];
short S101[59049];
short S8x4[6561*4];
short S7654[2187+729+243+81];
} Eval_weight;
enum {
W_C9 = offsetof(Eval_weight, C9) / sizeof(short) - 1, // -1 to load the data into hi-word
W_C10 = offsetof(Eval_weight, C10) / sizeof(short) - 1,
W_S100 = offsetof(Eval_weight, S100) / sizeof(short) - 1,
W_S101 = offsetof(Eval_weight, S101) / sizeof(short) - 1
};
__m256i FF = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[0]),
_mm256_set_epi32(W_C10, W_C10, W_C10, W_C10, W_C9, W_C9, W_C9, W_C9));
__m256i DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w, FF, 2);
__m256i SS = _mm256_srai_epi32(DD, 16); // sign extend
FF = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[1]),
_mm256_set_epi32(W_S101, W_S101, W_S101, W_S101, W_S100, W_S100, W_S100, W_S100));
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w, FF, 2);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(DD, 16));
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *)(w->S8x4 - 1), _mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[2]), 2);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(DD, 16));
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *)(w->S7654 - 1), _mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(*(__m128i *) &eval->feature.us[30]), 2);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(DD, 16));
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *)(w->S7654 - 1), _mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(*(__m128i *) &eval->feature.us[38]), 2);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(DD, 16));
__m128i S = _mm_add_epi32(_mm256_castsi256_si128(SS), _mm256_extracti128_si256(SS, 1));
__m128i D = _mm_i32gather_epi32((int *)(w->S8x4 - 1), _mm_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[3]), 2);
S = _mm_add_epi32(S, _mm_srai_epi32(D, 16));
S = _mm_hadd_epi32(S, S);
sum = _mm_cvtsi128_si32(S) + _mm_extract_epi32(S, 1);
return sum + w->S8x4[eval->feature.us[28]] + w->S8x4[eval->feature.us[29]] + w->S0;
これをプロファイリングしてみると(予想されることだが)メモリアクセスで律速になっており、命令を減らすために(ときにキャッシュラインをまたぐ)余分なワードを読み捨てるのでは本末転倒かもしれないので、アラインされた 32ビットを読むように書き換えてみる。(4.5.5)
typedef struct Eval_weight {
int S0;
short C9[19683];
short C10[59049];
short S100[59049];
short S101[59049];
short S8x4[6561*4]; // align(4)
short S7654[2187+729+243+81]; // align(4)
} Eval_weight;
assert((offsetof(Eval_weight, S8x4) & 3) == 0 && (offsetof(Eval_weight, S7654) & 3) == 0);
enum {
W_C9 = offsetof(Eval_weight, C9) / sizeof(short),
W_C10 = offsetof(Eval_weight, C10) / sizeof(short),
W_S100 = offsetof(Eval_weight, S100) / sizeof(short)1,
W_S101 = offsetof(Eval_weight, S101) / sizeof(short)1
};
const __m256i one = _mm256_set1_epi32(1);
__m256i FF = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[0]),
_mm256_set_epi32(W_C10, W_C10, W_C10, W_C10, W_C9, W_C9, W_C9, W_C9));
__m256i B0 = _mm256_slli_epi32(_mm256_andnot_si256(FF, one), 4); // 16 for even, 0 for odd
__m256i DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w, _mm256_andnot_si256(one, FF), 2);
__m256i SS = _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sllv_epi32(DD, B0), 16); // select word and sign extend
FF = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[1]),
_mm256_set_epi32(W_S101, W_S101, W_S101, W_S101, W_S100, W_S100, W_S100, W_S100));
B0 = _mm256_slli_epi32(_mm256_andnot_si256(FF, one), 4);
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w, _mm256_andnot_si256(one, FF), 2);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sllv_epi32(DD, B0), 16));
FF = _mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[2]);
B0 = _mm256_slli_epi32(_mm256_andnot_si256(FF, one), 4);
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w->S8x4, _mm256_andnot_si256(one, FF), 2);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sllv_epi32(DD, B0), 16));
FF = _mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[4]);
B0 = _mm256_slli_epi32(_mm256_andnot_si256(FF, one), 4);
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w->S7654, _mm256_andnot_si256(one, FF), 2);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sllv_epi32(DD, B0), 16));
FF = _mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(
_mm_alignr_epi8(eval->feature.v8[5], eval->feature.v8[3], 12)); // f[45]..f[40] f[31] f[30]
B0 = _mm256_slli_epi32(_mm256_andnot_si256(FF, one), 4);
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w->S7654, _mm256_andnot_si256(one, FF), 2);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sllv_epi32(DD, B0), 16));
__m128i S = _mm_add_epi32(_mm256_castsi256_si128(SS), _mm256_extracti128_si256(SS, 1));
__m128i F = _mm_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[3]);
__m128i B = _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_andnot_si128(F, _mm256_castsi256_si128(one)), 4);
__m128i D = _mm_i32gather_epi32((int *) w->S8x4, _mm_andnot_si128(_mm256_castsi256_si128(one), F), 2);
S = _mm_add_epi32(S, _mm_srai_epi32(_mm_sllv_epi32(D, B), 16));
S = _mm_hadd_epi32(S, S);
sum = _mm_cvtsi128_si32(S) + _mm_extract_epi32(S, 1);
return sum + w->S8x4[eval->feature.us[28]] + w->S8x4[eval->feature.us[29]] + w->S0;
しかしこれでは命令増が多すぎるので、[0] を偶数 ply, [1] を奇数 ply 用に Eval_weight をインターリーブし、上下ワードの取り出しを一律にする。
Eval->feature の alignr もレジスタを圧迫するようなので元に戻す。
// [0] for even ply, [1] for odd, interleaved for aligned VPGATHERDD access (4.5.5)
typedef struct Eval_weight {
short S0[2];
short C9[19683][2];
short C10[59049][2];
short S100[59049][2];
short S101[59049][2];
short S8x4[6561*4][2];
short S7654[2187+729+243+81][2];
} Eval_weight;
static const unsigned long long shift_even[2] = { 16, 0 };
enum {
W_C9 = offsetof(Eval_weight, C9) / 4,
W_C10 = offsetof(Eval_weight, C10) / 4,
W_S100 = offsetof(Eval_weight, S100) / 4,
W_S101 = offsetof(Eval_weight, S101) / 4
};
int b0 = ply & 1; // even/odd ply interleaved for aligned VPGATHERDD access (4.5.5)
const Eval_weight *w = *EVAL_WEIGHT + (ply >> 1);
__m128i SW = _mm_loadl_epi64((__m128i *)(shift_even + b0)); // 16 for even, 0 for odd
__m256i FF = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[0]),
_mm256_set_epi32(W_C10, W_C10, W_C10, W_C10, W_C9, W_C9, W_C9, W_C9));
__m256i DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w, FF, 4);
__m256i SS = _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sll_epi32(DD, SW), 16); // select word and sign extend
FF = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[1]),
_mm256_set_epi32(W_S101, W_S101, W_S101, W_S101, W_S100, W_S100, W_S100, W_S100));
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w, FF, 4);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sll_epi32(DD, SW), 16));
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w->S8x4, _mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[2]), 4);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sll_epi32(DD, SW), 16));
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w->S7654, _mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(*(__m128i *) &eval->feature.us[30]), 4);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sll_epi32(DD, SW), 16));
DD = _mm256_i32gather_epi32((int *) w->S7654, _mm256_cvtepu16_epi32(*(__m128i *) &eval->feature.us[38]), 4);
SS = _mm256_add_epi32(SS, _mm256_srai_epi32(_mm256_sll_epi32(DD, SW), 16));
__m128i S = _mm_add_epi32(_mm256_castsi256_si128(SS), _mm256_extracti128_si256(SS, 1));
__m128i D = _mm_i32gather_epi32((int *) w->S8x4, _mm_cvtepu16_epi32(eval->feature.v8[3]), 4);
S = _mm_add_epi32(S, _mm_srai_epi32(_mm_sll_epi32(D, SW), 16));
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6996764/fastest-way-to-do-horizontal-sse-vector-sum-or-other-reduction
S = _mm_add_epi32(S, _mm_unpackhi_epi64(S, S));
sum = _mm_cvtsi128_si32(_mm_add_epi32(S, _mm_shufflelo_epi16(S, 0x4e)));
w = (Eval_weight *)(w->S0 + b0);
return sum + *(w->S8x4[eval->feature.us[28]]) + *(w->S8x4[eval->feature.us[29]]) + *(w->S0);
unsigned long long board_get_hash_code(const Board *board)
{
unsigned long long h1, h2;
const unsigned char *p = (const unsigned char*)board;
h1 = hash_rank[0][p[0]];
h2 = hash_rank[1][p[1]];
h1 ^= hash_rank[2][p[2]];
h2 ^= hash_rank[3][p[3]];
h1 ^= hash_rank[4][p[4]];
h2 ^= hash_rank[5][p[5]];
h1 ^= hash_rank[6][p[6]];
h2 ^= hash_rank[7][p[7]];
h1 ^= hash_rank[8][p[8]];
h2 ^= hash_rank[9][p[9]];
h1 ^= hash_rank[10][p[10]];
h2 ^= hash_rank[11][p[11]];
h1 ^= hash_rank[12][p[12]];
h2 ^= hash_rank[13][p[13]];
h1 ^= hash_rank[14][p[14]];
h2 ^= hash_rank[15][p[15]];
return h1 ^ h2;
}
SSE4.2 と armv8.1 で、CPU 命令として CRC32C が追加されていて、これをハッシュ関数に使うと数クロックで 16 バイトに対するハッシュ値を得られる。 (4.5.0)
#if defined(__SSE4_2__) || defined(__AVX__)
#ifdef HAS_CPU_64
#define crc32c_u64(crc,d) _mm_crc32_u64((crc),(d))
#else
#define crc32c_u64(crc,d) _mm_crc32_u32(_mm_crc32_u32((crc),(d)),((d)>>32))
#endif
#elif defined(__ARM_FEATURE_CRC32)
#define crc32c_u64(crc,d) __crc32cd((crc),(d))
#else
unsigned int crc32c_u64(unsigned int crc, unsigned long long data)
{
crc ^= (unsigned int) data;
crc = crc32c_table[3][crc & 0xff] ^
crc32c_table[2][(crc >> 8) & 0xff] ^
crc32c_table[1][(crc >> 16) & 0xff] ^
crc32c_table[0][crc >> 24];
crc ^= (unsigned int) (data >> 32);
return crc32c_table[3][crc & 0xff] ^
crc32c_table[2][(crc >> 8) & 0xff] ^
crc32c_table[1][(crc >> 16) & 0xff] ^
crc32c_table[0][crc >> 24];
}
#endif
unsigned long long board_get_hash_code(const Board *board)
{
unsigned long long crc;
crc = crc32c_u64(0, board->player);
return (crc << 32) | crc32c_u64(crc, board->opponent);
}
const HashData HASH_DATA_INIT = {{{ 0, 0, 0, 0 }}, -SCORE_INF, SCORE_INF, { NOMOVE, NOMOVE }};
void hash_cleanup(HashTable *hash_table)
{
unsigned int i, imax = hash_table->hash_mask + HASH_N_WAY;
Hash *pHash = hash_table->hash;
assert(hash_table != NULL && hash_table->hash != NULL);
info("< cleaning hashtable >\n");
for (i = 0; i <= imax; ++i, ++pHash) {
pHash->board.player = pHash->board.opponent = 0;
pHash->data = HASH_DATA_INIT;
}
hash_table->date = 0;
}
ハッシュエントリのサイズは現在の実装では 24 バイトなので、4 エントリ 96 バイト (SSE では 2 エントリ 48 バイト) をベクターレジスターを使って書き込む。 (4.5.1)
i = 0;
if ((sizeof(Hash) == 24) && (((uintptr_t) pHash & 0x1f) == 0) && (imax >= 7)) {
for (; i < 4; ++i, ++pHash) {
pHash->board.player = pHash->board.opponent = 0;
pHash->data = HASH_DATA_INIT;
}
#ifdef __AVX__
__m256i d0 = _mm256_load_si256((__m256i *)(pHash - 4));
__m256i d1 = _mm256_load_si256((__m256i *)(pHash - 4) + 1);
__m256i d2 = _mm256_load_si256((__m256i *)(pHash - 4) + 2);
for (i = 4; i <= imax - 3; i += 4, pHash += 4) {
_mm256_stream_si256((__m256i *) pHash, d0);
_mm256_stream_si256((__m256i *) pHash + 1, d1);
_mm256_stream_si256((__m256i *) pHash + 2, d2);
}
#else
__m128i d0 = _mm_load_si128((__m128i *)(pHash - 4));
__m128i d1 = _mm_load_si128((__m128i *)(pHash - 4) + 1);
__m128i d2 = _mm_load_si128((__m128i *)(pHash - 4) + 2);
for (i = 4; i <= imax - 1; i += 2, pHash += 2) {
_mm_stream_si128((__m128i *) pHash, d0);
_mm_stream_si128((__m128i *) pHash + 1, d1);
_mm_stream_si128((__m128i *) pHash + 2, d2);
}
#endif
_mm_sfence();
}
for (; i <= imax; ++i, ++pHash) {
pHash->board.player = pHash->board.opponent = 0;
pHash->data = HASH_DATA_INIT;
}
hash_table->date = 0;
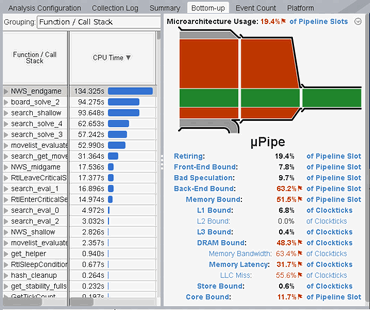
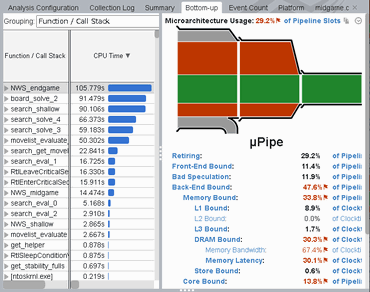 NWS_endgame 中に
prefetch†
を入れることで LLC Miss がなくなって DRAM Bound は約 30% になり、その分高速化できた。 (4.5.1)
NWS_endgame 中に
prefetch†
を入れることで LLC Miss がなくなって DRAM Bound は約 30% になり、その分高速化できた。 (4.5.1)
時間がかかる search_get_movelist (並べ替えと探索の2回使うため、すべての着手可能な手について flip を求めておく) の間に、
L1 キャッシュラインは 64 バイトなので、 HASH_N_WAY (4 エントリ) の最初と最後をプリフェッチする。
inline void hash_prefetch(HashTable *hashtable, unsigned long long hashcode) {
Hash *p = hashtable->hash + (hashcode & hashtable->hash_mask);
#ifdef hasSSE2
_mm_prefetch((char const *) p, _MM_HINT_T0);
_mm_prefetch((char const *)(p + HASH_N_WAY - 1), _MM_HINT_T0);
#elif defined(__ARM_ACLE)
__pld(p);
__pld(p + HASH_N_WAY - 1);
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
__builtin_prefetch(p);
__builtin_prefetch(p + HASH_N_WAY - 1);
#endif
}
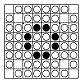
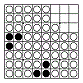
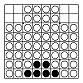 bitboard の埋まっている列の求め方はこちら。
bitboard の埋まっている列の求め方はこちら。
論文中では探索数が半減するとなっているが、前項の通り置換表の参照にもコストはかかるので、Edax では置換表を使うのは8か所空き以上になっており、
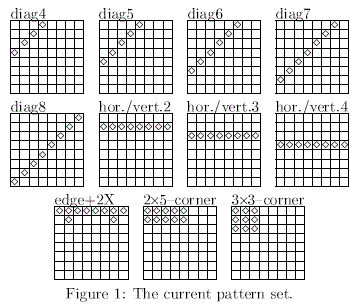
右図にいくつかの例を挙げるが8方向とも埋まっているマスは限られているため、実際の探索数の節減は 1 〜 2% にとどまるようだ。
それ以上の空きではさらに急減するので、8・9 か所空きのみに導入している。 (4.5.0)
また Edax の置換表は反復深化・拡幅の過程で前回の探索結果を保持するためにも使われているが、完全読み以外では度外石の処理コストが見合わないし、
またコードの変更も大きくなるので、完全読みのみに導入している。
Stability Cutoff† の試行を行ったときに限ればわずかな追加負担で度外石を求められるが、SC の試行はα値が大きい (αカットに必要な確定石が少ない) ときにしか行われないので、効果はさらに小さくなる。
またα値が変わると置換表に書かれる盤面が変わる可能性もあるが、α値が変わる頻度は低く実用上大きな支障はないようだ。
solid_opp = full[4] & hashboard.opponent; // full[4] = all full
#ifndef POPCOUNT
if (solid_opp)
#endif
{
hashboard.player ^= solid_opp; // normalize solid to player
hashboard.opponent ^= solid_opp;
ofssolid = bit_count(solid_opp) * 2; // hash score is ofssolid grater than real
}
手順前後の同形の大半は 3手または 4手で生じるので、ノードのスレッド分割が生じてから十分に深い局面であれば、
同期処理が不要な、スレッドごとにローカルに持った置換表でも十分な効果が期待できる。
空き数が少ない局面では再探索のコストも相対的に小さくなるため、衝突による多少の欠落があっても置換表の処理を軽くする方がバランスがよくなる。
このため共有置換表の 4-way (同じハッシュ値に対し価値の高い順に 4局面を残す) に対し、スレッドローカル置換表は単純な後着優先のダイレクトマッピングにしている
(途中のクリア不要でずっと使い回せる)。
通常の置換表のサイズはメインメモリの範囲で大きくすると深い探索を高速化できることがあるが、スレッドローカル置換表は主に局所的な手順前後を扱うのであまり大きくする必要はない。
CPU キャッシュに収まる程度が望ましく (4.5.5 ではスレッドあたり 1024 entry = 24KB) 、従って prefetch も不要。
10か所空きからスレッドローカル置換表を使うことにしたが、置換表処理の軽量化により 7か所空きにも適用できるようになり、トータルで 10%程度高速化できた。
偶数理論は終盤に盤面上に複数の空地ができたとき、奇数空きの空地に先着すると、その空地に交互に打った時に手止まりが打て有利になるという経験則。
7か所空きから5か所空きまでは search_shallow 内で、盤面を4象限に分けてそれぞれの空きの偶奇をパリティフラグとして持ち、奇数空き、偶数空きの2回ループしている。
(8か所空き以上では move_evaluate 内で考慮)
次のコードは4か所空きのためのもので、空地の分配は 4, 3-1, 2-2, 2-1-1, 1-1-1-1 のいずれかになっており、このうち 2-1-1 のみ並べ替えが必要になる。
3か所空きでは 3, 2-1, 1-1-1 のいずれかで、2-1 の場合に並べ替えが必要になる。
// parity based move sorting.
// The following hole sizes are possible:
// 4 - 1 3 - 2 2 - 1 1 2 - 1 1 1 1
// Only the 1 1 2 case needs move sorting.
if (!(search->parity & QUADRANT_ID[x1])) {
if (search->parity & QUADRANT_ID[x2]) {
if (search->parity & QUADRANT_ID[x3]) { // case 1(x2) 1(x3) 2(x1 x4)
int tmp = x1; x1 = x2; x2 = x3; x3 = tmp;
} else { // case 1(x2) 1(x4) 2(x1 x3)
int tmp = x1; x1 = x2; x2 = x4; x4 = x3; x3 = tmp;
}
} else if (search->parity & QUADRANT_ID[x3]) { // case 1(x3) 1(x4) 2(x1 x2)
int tmp = x1; x1 = x3; x3 = tmp; tmp = x2; x2 = x4; x4 = tmp;
}
} else {
if (!(search->parity & QUADRANT_ID[x2])) {
if (search->parity & QUADRANT_ID[x3]) { // case 1(x1) 1(x3) 2(x2 x4)
int tmp = x2; x2 = x3; x3 = tmp;
} else { // case 1(x1) 1(x4) 2(x2 x3)
int tmp = x2; x2 = x4; x4 = x3; x3 = tmp;
}
}
}
| 0 | 1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 |
| 08 | 09 | 0A | 0B | 0C | 0D | 0E | 0F | |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | |
| 18 | 19 | 1A | 1B | 1C | 1D | 1E | 1F | |
| 1 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 2A | 2B | 2C | 2D | 2E | 2F | |
| 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | |
| 38 | 39 | 3A | 3B | 3C | 3D | 3E | 3F | |
この情報を元に、4か所空きと3か所空きの両方の並べ替えを行うことができる。
ただし元コードでは4か所空きから残り3か所空きを呼び出すとき、並べ替える前の順で渡していることに注意が必要。
(Empty List は隅優先の固定順で並んでおり、パリティ同格の場合は元の順番を維持する。)
並べ替えを一度に行ってしまうと、3番目と4番目が入れ替わっている場合がある。
static const unsigned char parity_case[64] = { /* x4x3x2x1 = */
/*0000*/ 0, /*0001*/ 0, /*0010*/ 1, /*0011*/ 9, /*0100*/ 2, /*0101*/ 10, /*0110*/ 11, /*0111*/ 3,
/*0002*/ 0, /*0003*/ 0, /*0012*/ 0, /*0013*/ 0, /*0102*/ 4, /*0103*/ 4, /*0112*/ 5, /*0113*/ 5,
/*0020*/ 1, /*0021*/ 0, /*0030*/ 1, /*0031*/ 0, /*0120*/ 6, /*0121*/ 7, /*0130*/ 6, /*0131*/ 7,
/*0022*/ 9, /*0023*/ 0, /*0032*/ 0, /*0033*/ 9, /*0122*/ 8, /*0123*/ 0, /*0132*/ 0, /*0133*/ 8,
/*0200*/ 2, /*0201*/ 4, /*0210*/ 6, /*0211*/ 8, /*0300*/ 2, /*0301*/ 4, /*0310*/ 6, /*0311*/ 8,
/*0202*/ 10, /*0203*/ 4, /*0212*/ 7, /*0213*/ 0, /*0302*/ 4, /*0303*/ 10, /*0312*/ 0, /*0313*/ 7,
/*0220*/ 11, /*0221*/ 5, /*0230*/ 6, /*0231*/ 0, /*0320*/ 6, /*0321*/ 0, /*0330*/ 11, /*0331*/ 5,
/*0222*/ 3, /*0223*/ 5, /*0232*/ 7, /*0233*/ 8, /*0322*/ 8, /*0323*/ 7, /*0332*/ 5, /*0333*/ 3
};
paritysort = parity_case[((x3 ^ x4) & 0x24) + ((((x2 ^ x4) & 0x24) * 2 + ((x1 ^ x4) & 0x24)) >> 2)];
SSE / AVX / Neon が利用できるとき、空き位置をベクターレジスターに持つと、並べ替えにシャッフル命令を使うことができる。
static const union V4SI shuf_mask[] = { // make search order identical to 4.4.0
{{ 0x03020100, 0x02030100, 0x01030200, 0x00030201 }}, // 0: 1(x1) 3(x2 x3 x4), 1(x1) 1(x2) 2(x3 x4), 1 1 1 1, 4
{{ 0x03020100, 0x02030100, 0x01020300, 0x00020301 }}, // 1: 1(x2) 3(x1 x3 x4)
{{ 0x03010200, 0x02010300, 0x01030200, 0x00010302 }}, // 2: 1(x3) 3(x1 x2 x4)
{{ 0x03000201, 0x02000301, 0x01000302, 0x00030201 }}, // 3: 1(x4) 3(x1 x2 x3)
{{ 0x03010200, 0x01030200, 0x02030100, 0x00030201 }}, // 4: 1(x1) 1(x3) 2(x2 x4)
{{ 0x03000201, 0x00030201, 0x02030100, 0x01030200 }}, // 5: 1(x1) 1(x4) 2(x2 x3)
{{ 0x02010300, 0x01020300, 0x03020100, 0x00030201 }}, // 6: 1(x2) 1(x3) 2(x1 x4)
{{ 0x02000301, 0x00020301, 0x03020100, 0x01030200 }}, // 7: 1(x2) 1(x4) 2(x1 x3)
{{ 0x01000302, 0x00010302, 0x03020100, 0x02030100 }}, // 8: 1(x3) 1(x4) 2(x1 x2)
{{ 0x03020100, 0x02030100, 0x01000302, 0x00010302 }}, // 9: 2(x1 x2) 2(x3 x4)
{{ 0x03010200, 0x02000301, 0x01030200, 0x00020301 }}, // 10: 2(x1 x3) 2(x2 x4)
{{ 0x03000201, 0x02010300, 0x01020300, 0x00030201 }} // 11: 2(x1 x4) 2(x2 x3)
};
empties_series = _mm_cvtsi32_si128((x1 << 24) | (x2 << 16) | (x3 << 8) | x4);
empties_series = _mm_shuffle_epi8(empties_series, shuf_mask[paritysort].v4);
acepck 氏の Egaroucid への pull request によると、ここでは単純な偶数理論より1か所空きを優先した方がさらに効率がよいようだ。
1か所空きは確実に手止まりになるのでこれはうなずける。
static const V4SI shuf_mask[] = { // 4.5.5: prefer 1 empty over 3 empties
{{ 0x03020100, 0x02030100, 0x01030200, 0x00030201 }}, // 0: 1(x1) 3(x2 x3 x4), 1(x1) 1(x2) 2(x3 x4), 1 1 1 1, 4
{{ 0x02030100, 0x03020100, 0x01030200, 0x00030201 }}, // 1: 1(x2) 3(x1 x3 x4)
{{ 0x01030200, 0x03020100, 0x02030100, 0x00030201 }}, // 2: 1(x3) 3(x1 x2 x4)
{{ 0x00030201, 0x03020100, 0x02030100, 0x01030200 }}, // 3: 1(x4) 3(x1 x2 x3)
並べ替えのケースが増えると SIMD を使わない場合でも、シャッフル(この例では2ビットづつのマスク)をシミュレートした方が、計算は増えるが分岐が少なくなる。
int x1 = (empties3 >> ((shuf3 & 0x30) >> 1)) & 0xFF; int x2 = (empties3 >> ((shuf3 & 0x0C) << 1)) & 0xFF; int x3 = (empties3 >> ((shuf3 & 0x03) * 8)) & 0xFF;
static int board_solve_2(Board *board, int alpha, const int x1, const int x2, Search *search)
{
Board next[1];
register int score, bestscore;
const int beta = alpha + 1;
SEARCH_UPDATE_INTERNAL_NODES();
if ((NEIGHBOUR[x1] & board->opponent) && board_next(board, x1, next)) { // (84%/87%)
SEARCH_UPDATE_INTERNAL_NODES();
bestscore = board_score_1(next, beta, x2);
} else bestscore = -SCORE_INF;
if (bestscore < beta) { // (63%)
if ((NEIGHBOUR[x2] & board->opponent) && board_next(board, x2, next)) { // (92%/91%)
SEARCH_UPDATE_INTERNAL_NODES();
score = board_score_1(next, beta, x1);
if (score > bestscore) bestscore = score;
}
// pass
if (bestscore == -SCORE_INF) { // (17%)
if ((NEIGHBOUR[x1] & board->player) && board_pass_next(board, x1, next)) { // (100%/95%)
SEARCH_UPDATE_INTERNAL_NODES();
bestscore = -board_score_1(next, -alpha, x2);
} else bestscore = SCORE_INF;
if (bestscore > alpha) { // (20%)
if ((NEIGHBOUR[x2] & board->player) && board_pass_next(board, x2, next)) { // (100%/99%)
SEARCH_UPDATE_INTERNAL_NODES();
score = -board_score_1(next, -alpha, x1);
if (score < bestscore) bestscore = score;
}
// gameover
if (bestscore == SCORE_INF) bestscore = board_solve(board, 2);
}
}
}
return bestscore;
}
score2 = score - o_flip - (int)((o_flip > 0) | (score <= 0)) * 2;は手番側がパスの時、相手が打てるか、(最後の空きを仮に手番側に加えた)石差が0以下なら相手に最後の空きを加える処理で、 この書き方でも SETcc を使った分岐のないコードになるが、比較 - SETcc - ゼロ拡張と3命令かかる(APX では改善された)ため、 符号ビットから結果が得られるように書き換えると(コンパイラによるが)少し短いコードになる。 (4.5.3)
score2 = score - o_flip - (int)((-o_flip | (score - 1)) < 0) * 2;
x = pos & 0x07; y8 = pos & 0x38; t = _mm256_movemask_epi8(_mm256_sub_epi8(_mm256_setzero_si256(), _mm256_and_si256(PP, mask_vdhd[pos].v4))) op_flip = COUNT_FLIP[x * 256 + ((P >> y8) & 0xFF)]; // h op_flip += COUNT_FLIP[y8 * 32 + (t >> 24)]; // v op_flip += COUNT_FLIP[cf_ofs_d[pos][1] + ((t >> 16) & 0xFF)]; // d op_flip += COUNT_FLIP[cf_ofs_d[pos][0] + (t & 0xFF)]; // d o_flips = op_flip >> 8; p_flips = op_flip & 0xFF;ここでも cf_ofs_d を 32 ビットにして上位ワードと下位ワードにそれぞれの斜め方向の開始オフセットを入れると、表引きを1回減らせる。
op_flip = COUNT_FLIP[x * 256 + ((P >> y8) & 0xFF)]; // h op_flip += COUNT_FLIP[y8 * 32 + (t >> 24)]; // v t = cf_ofs_d[pos] + (t & 0x00FF00FF); // 0d0d op_flip += COUNT_FLIP[t & 0xFFFF]; op_flip += COUNT_FLIP[t >> 16];逐次処理との比較では、手番側が打てる場合の表引き1回とテーブルサイズ(CPU キャッシュ消費)の小さなコスト増に対し、パスだった場合は相手側の処理が丸々無くなりゲインは大きいが、 やはりパスの確率が低い(20% 程度)のでトータルでの損得は環境による。
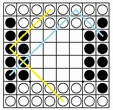 表引きの並列化はビットを集めて表を引くすべての Last Flip に適用できるが、図の黒のマスでは斜め方向を BMI2 PEXT,
横方向を (水平加算の代用として) Kindergarten, 白のマスでは横方向を PEXT, 斜め方向を Kindergarten でビットを集めると (縦はいずれも PEXT),
いずれも斜め方向は 結合 して表引きが行え、最終手でほとんど現れない中央の 16マスを除き
すべて 8 ビット× 3 の表引きに帰着できる。この場合は (中央 16 マスを例外として) 長さによる場合分けも考えなくてよい。
表引きの並列化はビットを集めて表を引くすべての Last Flip に適用できるが、図の黒のマスでは斜め方向を BMI2 PEXT,
横方向を (水平加算の代用として) Kindergarten, 白のマスでは横方向を PEXT, 斜め方向を Kindergarten でビットを集めると (縦はいずれも PEXT),
いずれも斜め方向は 結合 して表引きが行え、最終手でほとんど現れない中央の 16マスを除き
すべて 8 ビット× 3 の表引きに帰着できる。この場合は (中央 16 マスを例外として) 長さによる場合分けも考えなくてよい。
static const uint64_t mask_pext[64] = { // merged diagonal for left/right edge, diag-9 for center box, horizontal otherwise
0x00000000000000ff, 0x00000000000000ff, 0x00000000000000ff, 0x00000000000000ff, 0x00000000000000ff, 0x00000000000000ff, 0x00000000000000ff, 0x00000000000000ff,
0x4020100804020102, 0x000000000000ff00, 0x000000000000ff00, 0x000000000000ff00, 0x000000000000ff00, 0x000000000000ff00, 0x000000000000ff00, 0x0204081020408040,
0x2010080402010204, 0x4020100804020408, 0x0000000102000810, 0x0000010204001020, 0x0001020408002040, 0x0102040810204080, 0x0204081020402010, 0x0408102040804020,
0x1008040201020408, 0x2010080402040810, 0x0000010200081020, 0x0001020400102040, 0x0102040810204080, 0x0204081000408000, 0x0408102040201008, 0x0810204080402010,
0x0804020102040810, 0x1008040204081020, 0x0001020008102040, 0x0102040810204080, 0x0204080020408000, 0x0408100040800000, 0x0810204020100804, 0x1020408040201008,
0x0402010204081020, 0x0804020408102040, 0x0102040810204080, 0x0204001020408000, 0x0408002040800000, 0x0810004080000000, 0x1020402010080402, 0x2040804020100804,
0x0201020408102040, 0x00ff000000000000, 0x00ff000000000000, 0x00ff000000000000, 0x00ff000000000000, 0x00ff000000000000, 0x00ff000000000000, 0x4080402010080402,
0xff00000000000000, 0xff00000000000000, 0xff00000000000000, 0xff00000000000000, 0xff00000000000000, 0xff00000000000000, 0xff00000000000000, 0xff00000000000000
};
static const uint64_t mask_kg[64] = { // merged diagonal for top/bottom edge or horizontal otherwise
0x8040201008040201, 0x0080402010080502, 0x0000804020110a04, 0x0000008041221408, 0x0000000182442810, 0x0000010204885020, 0x0001020408102040, 0x0102040810204080,
0x000000000000ff00, 0x8040201008040201, 0x00804020110a0400, 0x0000804122140800, 0x0000018244281000, 0x0001020488502000, 0x0102040810204080, 0x000000000000ff00,
0x0000000000ff0000, 0x0000000000ff0000, 0x0000000000ff0000, 0x0000000000ff0000, 0x0000000000ff0000, 0x0000000000ff0000, 0x0000000000ff0000, 0x0000000000ff0000,
0x00000000ff000000, 0x00000000ff000000, 0x00000000ff000000, 0x00000000ff000000, 0x00000000ff000000, 0x00000000ff000000, 0x00000000ff000000, 0x00000000ff000000,
0x000000ff00000000, 0x000000ff00000000, 0x000000ff00000000, 0x000000ff00000000, 0x000000ff00000000, 0x000000ff00000000, 0x000000ff00000000, 0x000000ff00000000,
0x0000ff0000000000, 0x0000ff0000000000, 0x0000ff0000000000, 0x0000ff0000000000, 0x0000ff0000000000, 0x0000ff0000000000, 0x0000ff0000000000, 0x0000ff0000000000,
0x00ff000000000000, 0x0102040810204080, 0x00040a1120408000, 0x0008142241800000, 0x0010284482010000, 0x0020508804020100, 0x8040201008040201, 0x00ff000000000000,
0x0102040810204080, 0x0205081020408000, 0x040a112040800000, 0x0814224180000000, 0x1028448201000000, 0x2050880402010000, 0x40a0100804020100, 0x8040201008040201
};
static const uint64_t mask_box_d7[] = { // diag-7 for center box
0x8040201008040201, 0x0080402010000402, 0x0000804020000804, 0x0000008040001008, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0x4020100800020100, 0x8040201008040201, 0x0080402000080402, 0x0000804000100804, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0x2010080002010000, 0x4020100004020100, 0x8040201008040201, 0x0080400010080402, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0x1008000201000000, 0x2010000402010000, 0x4020000804020100, 0x8040201008040201
};
op_flip = COUNT_FLIP[(pos & 0x38) * 32 + _pext_u64(P, 0x0101010101010101 << (pos & 0x07))]; op_flip += COUNT_FLIP[ofs_pext[pos] + _pext_u64(P, mask_pext[pos])]; op_flip += COUNT_FLIP[(pos & 0x07) * 256 + ((uint64_t)((P & mask_kg[pos]) * 0x0101010101010101) >> 56)]; if (0x00003c3c3c3c0000 & (1ULL << pos)) // last move in inner box (0%) op_flip += COUNT_FLIP[ofs_box_d7[pos - 18] + _pext_u64(P, mask_box_d7[pos - 18])];白のマスの斜めも PEXT でも結合できるが、ビット集めの結果が交錯するのでそれを考慮したマスごとの表が必要になる。
. . . * . . . . . . 0 . 1 . . . . 2 . . . 3 . . 4 . . . . . 5 . . . . . . . . 6
__m256i M = lmask[pos];
__m256i mO = _mm256_andnot_si256(P4, M);
__m256i F = _mm256_andnot_si256(_mm256_cmpeq_epi64(mO, M), mO); // clear if all O
M = rmask[pos];
mO = _mm256_andnot_si256(P4, M);
F = _mm256_or_si256(F, _mm256_andnot_si256(_mm256_cmpeq_epi64(mO, M), mO));
if (_mm256_testz_si256(F, _mm256_set1_epi64x(NEIGHBOUR[pos]))) { // pass (16%)
AVX512 が使える CPU では 8 方向同時に処理でき、BCST†
(embedded broadcast) やマスクレジスタも使って数命令で判定できる。
(_ktestz_mask8_u8 は後から追加された intrinsic で、古いコンパイラではサポートされていなかったり、残念なコードになることもある。
godbolt†)
__m512i M = lrmask[pos].v8;
__m512i mO = _mm512_andnot_epi64(P8, M);
__mmask8 fO = _mm512_test_epi64_mask(mO, _mm512_broadcastq_epi64(_mm_cvtsi64_si128(NEIGHBOUR[pos]))); // MSVC fails to use BCST for _mm512_set1_epi64
if (_ktestz_mask8_u8(_mm512_test_epi64_mask(P8, M), fO)) { // pass (16%)
だが Intel CPU には 512bit 命令を一つでも使うと一定時間
license based downclocking† がかかるものがあるので、ここだけなら ZMM を使うのは避けた方がいい。
(MSVC(2022) は prefer-vector-width に当たるオプションが無く、arch:AVX512 を指定するとコンパイラがメモリー転送などで ZMM を使うのでこの配慮は無意味だったが、
2024 年末に avx10/256 のために /vlen オプションとして追加された。)
__m256i M = lmask[pos];
__m256i F = _mm256_maskz_andnot_epi64(_mm256_test_epi64_mask(P4, M), P4, M); // clear if all O
M = rmask[pos];
// F = _mm256_mask_or_epi64(F, _mm256_test_epi64_mask(P4, M), F, _mm256_andnot_si256(P4, M));
F = _mm256_mask_ternarylogic_epi64(F, _mm256_test_epi64_mask(P4, M), P4, M, 0xF2);
if (_mm256_testz_si256(F, _mm256_set1_epi64x(NEIGHBOUR[pos]))) { // pass (16%)
手番側がパスのとき、相手の last flip を求めるため O ( = ~P ) にマスクをかけ、それにより返される石数を求めるが、
ここで求めた F は ~P & M で一方向がすべて O だったときにすべて P で置き換えたものになっており、
すべて O もすべて P も返る石は 0 なので、F をそのまま流用することができる。
// t = _cvtmask32_u32(_mm256_cmpneq_epi8_mask(_mm256_andnot_si256(P4, lM), _mm256_andnot_si256(P4, rM))); t = _cvtmask32_u32(_mm256_test_epi8_mask(F, F)); // all O = all P = 0 fliplazy high/low cut-off を使った NWS (Null Window Search) では、
| Haswell | Skylake | Icelake | Sapphire Rapids | Zen2 | Zen3 | Zen4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4 | C5 | C6i | C7i | C5a | C6a | C7a | ||
| SSE movemask | 2.979 | 2.672 | 2.546 | 2.482 | 3.006 | 2.349 | 2.199 | modern |
| AVX2 movemask | 2.985 | 2.664 | 2.541 | 2.491 | 3.013 | 2.358 | 2.200 | modern -DAVXLASTFLIP |
| AVX2 movemask lazy high cut | 2.984 | 2.656 | 2.517 | 2.521 | 3.030 | 2.357 | 2.206 | modern -DLASTFLIP_HIGHCUT |
| AVX2 movemask simul | 2.989 | 2.666 | 2.543 | 2.487 | 3.038 | 2.348 | 2.199 | modern -DSIMULLASTFLIP |
| BMI2 PEXT | 2.989 | 2.662 | 2.545 | 2.482 | 4.032 | 2.368 | 2.202 | modern -DLAST_FLIP_COUNTER=COUNT_LAST_FLIP_BMI2 |
| AVX512-256 lazy cut off | N/A | 2.591 | 2.333 | 2.378 | N/A | N/A | 2.121 | avx512 -DLASTFLIP_HIGHCUT |
| AVX512-256 simul | 2.614 | 2.383 | 2.412 | 2.114 | avx512 -DSIMULLASTFLIP | |||
| AVX512-512 simul | 2.714 | 2.475 | 2.511 | 2.148 | avx512 -DSIMULLASTFLIP512 | |||
| AVX512-256 movemask | 2.602 | 2.369 | 2.395 | 2.145 | avx512 -DLAST_FLIP_COUNTER=COUNT_LAST_FLIP_SSE | |||
| AVX512-256 PEXT | 2.591 | 2.349 | 2.393 | 2.146 | avx512 -DLAST_FLIP_COUNTER=COUNT_LAST_FLIP_BMI2 |
modern (AVX2) ビルド間の差は (Zen2 の PEXT を除き) わずかだが、新しい CPU ほど演算量が増えても分岐を減らし並列度を高めた方がいい傾向がうかがえる。
(AVX2 movemask simul のコンパイル結果には前述のとおりパスの分岐が含まれるが、lazy low cut の分岐は減っている)
AVX512 ビルドはこの測定では全 CPU の平均で lazy cut off (High/Low) + Flip が最速だったが、4.5.4 では前述の表引きの並列化により PEXT も互角になった。
AVX512 が使える CPU には PEXT が遅いものはなく、安心して使える。
512bit 演算は現時点ではすべての CPU で 256bit 並列より遅くなっている。
/** Loop over all empty squares on even quadrants */
#define foreach_even_empty(empty, list, parity)\
for ((empty) = (list)->next; (empty)->next; (empty) = (empty)->next) if ((parity & empty->quadrant) == 0)
/** Loop over all empty squares on odd quadrants */
#define foreach_odd_empty(empty, list, parity)\
for ((empty) = (list)->next; (empty)->next; (empty) = (empty)->next) if (parity & empty->quadrant)
static int search_shallow(Search *search, const int alpha)
{
Board *board = search->board;
SquareList *empty;
Move move;
int score, bestscore = -SCORE_INF;
const int beta = alpha + 1;
assert(SCORE_MIN <= alpha && alpha <= SCORE_MAX);
assert(0 <= search->n_empties && search->n_empties <= DEPTH_TO_SHALLOW_SEARCH);
SEARCH_STATS(++statistics.n_NWS_shallow);
SEARCH_UPDATE_INTERNAL_NODES();
// stability cutoff
if (search_SC_NWS(search, alpha, &score)) return score;
if (search->parity > 0 && search->parity < 15) {
foreach_odd_empty (empty, search->empties, search->parity) {
if ((NEIGHBOUR[empty->x] & board->opponent)
&& board_get_move(board, empty->x, &move)) {
search_update_endgame(search, &move);
if (search->n_empties == 4) score = -search_solve_4(search, -beta);
else score = -search_shallow(search, -beta);
search_restore_endgame(search, &move);
if (score >= beta) return score;
else if (score > bestscore) bestscore = score;
}
}
foreach_even_empty (empty, search->empties, search->parity) {
if ((NEIGHBOUR[empty->x] & board->opponent)
&& board_get_move(board, empty->x, &move)) {
search_update_endgame(search, &move);
if (search->n_empties == 4) score = -search_solve_4(search, -beta);
else score = -search_shallow(search, -beta);
search_restore_endgame(search, &move);
if (score >= beta) return score;
else if (score > bestscore) bestscore = score;
}
}
} else {
foreach_empty (empty, search->empties) {
if ((NEIGHBOUR[empty->x] & board->opponent)
&& board_get_move(board, empty->x, &move)) {
search_update_endgame(search, &move);
if (search->n_empties == 4) score = -search_solve_4(search, -beta);
else score = -search_shallow(search, -beta);
search_restore_endgame(search, &move);
if (score >= beta) return score;
else if (score > bestscore) bestscore = score;
}
}
}
// no move
if (bestscore == -SCORE_INF) {
if (can_move(board->opponent, board->player)) { // pass
search_pass_endgame(search);
bestscore = -search_shallow(search, -beta);
search_pass_endgame(search);
} else { // gameover
bestscore = search_solve(search);
}
}
assert(SCORE_MIN <= bestscore && bestscore <= SCORE_MAX);
return bestscore;
}
まず get_moves により打てる位置のビットボード moves を求めておく。
これ自体は get_moves のオーバーヘッドが加わる代わりに、打てない位置で flip を呼ばなくてよくなるので、
早い段階でαカットが起こる場合は差し引きマイナスだが、そうでなければプラスになることも期待できる。
パスの場合(レアケースだが)はループを回る必要がなくなる。
元コードの empty list は双方向リストになっており、search_update_endgame で remove, search_restore_endgame で restore が行われている。
8か所空き以上では事前評価による探索順の並べ替えが行われ、途中のノードの削除、挿入があるので双方向リストの方が便利だが、
ここではリストの順に処理されるので単方向リストで十分であり、順方向のリンクのみで削除・挿入を行う
(逆方向リンクには触らないので、戻るときには双方向リストが維持されている)。
元コードでは parity, n_empties, board も search_update_endgame, search_restore_endgame 内で処理されているが、
インライン展開するとループ外に出せるものもある。
const unsigned long long quadrant_mask[] = {
0x0000000000000000, 0x000000000F0F0F0F, 0x00000000F0F0F0F0, 0x00000000FFFFFFFF,
0x0F0F0F0F00000000, 0x0F0F0F0F0F0F0F0F, 0x0F0F0F0FF0F0F0F0, 0x0F0F0F0FFFFFFFFF,
0xF0F0F0F000000000, 0xF0F0F0F00F0F0F0F, 0xF0F0F0F0F0F0F0F0, 0xF0F0F0F0FFFFFFFF,
0xFFFFFFFF00000000, 0xFFFFFFFF0F0F0F0F, 0xFFFFFFFFF0F0F0F0, 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
};
static int search_shallow(Search *search, const int alpha, bool pass1)
{
unsigned long long moves, prioritymoves;
int x, prev, score, bestscore;
// const int beta = alpha + 1;
Board board0;
unsigned int parity0;
assert(SCORE_MIN <= alpha && alpha <= SCORE_MAX);
assert(0 <= search->eval.n_empties && search->eval.n_empties <= DEPTH_TO_SHALLOW_SEARCH);
SEARCH_STATS(++statistics.n_NWS_shallow);
SEARCH_UPDATE_INTERNAL_NODES(search->n_nodes);
// stability cutoff (try 15%, cut 5%)
if (search_SC_NWS(search, alpha, &score)) return score;
moves = get_moves(search->board.player, search->board.opponent);
if (moves == 0) { // pass (2%)
if (pass1) // gameover
return search_solve(search);
search_pass_endgame(search);
bestscore = -search_shallow(search, ~alpha, true);
search_pass_endgame(search);
return bestscore;
}
bestscore = -SCORE_INF;
board0 = search->board;
parity0 = search->eval.parity;
prioritymoves = moves & quadrant_mask[parity0];
if (prioritymoves == 0) // all even
prioritymoves = moves;
--search->eval.n_empties; // for next depth
do {
x = search->empties[prev = NOMOVE].next; // maintain single link only
do {
if (prioritymoves & x_to_bit(x)) { // (37%)
search->eval.parity = parity0 ^ QUADRANT_ID[x];
search->empties[prev].next = search->empties[x].next; // remove
board_next(&board0, x, &search->board);
if (search->eval.n_empties == 4) // (57%)
score = -search_solve_4(search, ~alpha);
else score = -search_shallow(search, ~alpha, false);
search->empties[prev].next = x; // restore
if (score > alpha) { // (40%)
search->board = board0;
search->eval.parity = parity0;
++search->eval.n_empties;
return score;
} else if (score > bestscore)
bestscore = score;
}
} while ((x = search->empties[prev = x].next) != NOMOVE);
} while ((prioritymoves = (moves ^= prioritymoves)));
search->board = board0;
search->eval.parity = parity0;
++search->eval.n_empties;
assert(SCORE_MIN <= bestscore && bestscore <= SCORE_MAX);
return bestscore; // (33%)
}
static void move_evaluate(Move *move, Search *search, const HashData *hash_data, const int sort_alpha, const int sort_depth)
{
Board *board = search->board;
HashData dummy[1];
if (move_wipeout(move, board)) move->score = (1 << 30);
else if (move->x == hash_data->move[0]) move->score = (1 << 29);
else if (move->x == hash_data->move[1]) move->score = (1 << 28);
else {
move->score = SQUARE_VALUE[move->x]; // square type
if (search->n_empties < 12 && search->parity & QUADRANT_ID[move->x]) move->score += w_low_parity; // parity
else if (search->n_empties < 21 && search->parity & QUADRANT_ID[move->x]) move->score += w_mid_parity; // parity
else if (search->n_empties < 30 && search->parity & QUADRANT_ID[move->x]) move->score += w_high_parity; // parity
if (sort_depth < 0) {
board_update(board, move);
SEARCH_UPDATE_ALL_NODES();
move->score += (36 - get_potential_mobility(board->player, board->opponent)) * w_potential_mobility; // potential mobility
move->score += get_corner_stability(board->opponent) * w_corner_stability; // corner stability
move->score += (36 - get_weighted_mobility(board->player, board->opponent)) * w_mobility; // real mobility
board_restore(board, move);
} else {
int selectivity = search->selectivity;
search->selectivity = NO_SELECTIVITY;
search_update_midgame(search, move);
// 中略
search_restore_midgame(search, move);
search->selectivity = selectivity;
}
}
}
void movelist_evaluate(MoveList *movelist, Search *search, const HashData *hash_data, const int alpha, const int depth)
{
int sort_depth, min_depth;
int sort_alpha;
Move *move;
min_depth = 9;
if (search->n_empties <= 27) min_depth += (30 - search->n_empties) / 3;
if (depth >= min_depth) {
sort_depth = (depth - 15) / 3;
if (hash_data && hash_data->upper < alpha) sort_depth -= 2;
if (search->n_empties >= 27) ++sort_depth;
if (sort_depth < 0) sort_depth = 0; else if (sort_depth > 6) sort_depth = 6;
} else {
sort_depth = -1;
}
sort_alpha = MAX(SCORE_MIN, alpha - SORT_ALPHA_DELTA);
foreach_move (move, movelist) {
move_evaluate(move, search, hash_data, sort_alpha, sort_depth);
}
}
この move_evaluate はα-βの効率を上げるために手の予備的な評価を行う部分で、34 行以下の move_list_evaluate からのみ (53 行から) 呼び出される。
void movelist_evaluate(MoveList *movelist, Search *search, const HashData *hash_data, const int alpha, const int depth)
{
Move *move;
int sort_depth, min_depth, sort_alpha, score, empties, parity_weight, org_selectivity;
HashData dummy;
unsigned long long P, O;
empties = search->eval.n_empties;
parity_weight = parity_weight_table[empties];
min_depth = min_depth_table[empties];
if (depth >= min_depth) {
sort_depth = (depth - 15) / 3;
if (hash_data && hash_data->upper < alpha) sort_depth -= 2;
if (empties >= 27) ++sort_depth;
if (sort_depth < 0) sort_depth = 0;
else if (sort_depth > 6) sort_depth = 6;
org_selectivity = search->selectivity;
search->selectivity = NO_SELECTIVITY;
sort_alpha = MAX(SCORE_MIN, alpha - SORT_ALPHA_DELTA);
move = movelist->move[0].next;
do {
// move_evaluate(move, search, hash_data, sort_alpha, sort_depth);
if (move_wipeout(move, &search->board)) score = (1 << 30);
else if (move->x == hash_data->move[0]) score = (1 << 29);
else if (move->x == hash_data->move[1]) score = (1 << 28);
else {
score = SQUARE_VALUE[move->x]; // square type
score += (search->eval.parity & QUADRANT_ID[move->x]) ? parity_weight : 0; // parity
search_update_midgame(search, move);
// 中略
search_restore_midgame(search, move);
}
move->score = score;
} while ((move = move->next));
search->selectivity = org_selectivity;
} else { // sort_depth = -1
move = movelist->move[0].next;
do {
// move_evaluate(move, search, hash_data, sort_alpha, -1);
if (move_wipeout(move, &search->board)) score = (1 << 30);
else if (move->x == hash_data->move[0]) score = (1 << 29);
else if (move->x == hash_data->move[1]) score = (1 << 28);
else {
score = SQUARE_VALUE[move->x]; // square type
score += (search->eval.parity & QUADRANT_ID[move->x]) ? parity_weight : 0; // parity
// board_update(&search->board, move);
O = search->board.player ^ (move->flipped | x_to_bit(move->x));
P = search->board.opponent ^ move->flipped;
SEARCH_UPDATE_ALL_NODES(search->n_nodes);
score += (36 - get_potential_mobility(P, O)) * w_potential_mobility; // potential mobility
score += get_corner_stability(O) * w_corner_stability; // corner stability
score += (36 - get_weighted_mobility(P, O)) * w_mobility; // real mobility
// board_restore(&search->board, move);
}
move->score = score;
} while ((move = move->next));
}
}
#ifdef __X86_64__
#define packA1A8(X) ((((X) & 0x0101010101010101ULL) * 0x0102040810204080ULL) >> 56)
#define packH1H8(X) ((((X) & 0x8080808080808080ULL) * 0x0002040810204081ULL) >> 56)
#else
#define packA1A8(X) (((((unsigned int)(X) & 0x01010101u) + (((unsigned int)((X) >> 32) & 0x01010101u) << 4)) * 0x01020408u) >> 24)
#define packH1H8(X) (((((unsigned int)((X) >> 32) & 0x80808080u) + (((unsigned int)(X) & 0x80808080u) >> 4)) * 0x00204081u) >> 24)
#endif
static inline unsigned long long get_stable_edge(const unsigned long long P, const unsigned long long O)
{
// compute the exact stable edges (from precomputed tables)
return edge_stability[P & 0xff][O & 0xff]
| ((unsigned long long)edge_stability[P >> 56][O >> 56]) << 56
| A1_A8[edge_stability[packA1A8(P)][packA1A8(O)]]
| H1_H8[edge_stability[packH1H8(P)][packH1H8(O)]];
}
int get_edge_stability(const unsigned long long P, const unsigned long long O)
{
return bit_count(get_stable_edge(P, O));
}
縦方向のビット集めは SSE なら PMOVMSKB でできるし、横方向は (CPU でも軽い処理ではあるが) そのついでに PUNPCKLBW で P と O を連結した
16 ビットを取り出すこともできる。 (表は 256 * 256 の1次元に変更)
static inline unsigned long long get_stable_edge(const unsigned long long P, const unsigned long long O)
{
// compute the exact stable edges (from precomputed tables)
unsigned long long stable_edge;
__v2di P0 = _mm_cvtsi64_si128(P);
__v2di O0 = _mm_cvtsi64_si128(O);
__v2di PO = _mm_unpacklo_epi8(O0, P0);
stable_edge = edge_stability[_mm_extract_epi16(PO, 0)]
| ((unsigned long long) edge_stability[_mm_extract_epi16(PO, 7)] << 56);
PO = _mm_unpacklo_epi64(O0, P0);
stable_edge |= A1_A8[edge_stability[_mm_movemask_epi8(_mm_slli_epi64(PO, 7))]]
| (A1_A8[edge_stability[_mm_movemask_epi8(PO)]] << 7);
return stable_edge;
}
ビット集めの反対のビット配りは BMI2 で追加された PDEP を使えば簡単にできるが、PEXT と同じく ZEN2 までの AMD では非常に遅い。#if 0 // defined(__BMI2__) && defined(HAS_CPU_64) && !defined(__bdver4__) && !defined(__znver1__) && !defined(__znver2__) // pdep is slow on AMD before Zen3 #define unpackA1A8(x) _pdep_u64((x), 0x0101010101010101) #define unpackH1H8(x) _pdep_u64((x), 0x8080808080808080) #else #define unpackA1A8(x) (((unsigned long long)((((x) >> 4) * 0x00204081) & 0x01010101) << 32) | ((((x) & 0x0f) * 0x00204081) & 0x01010101)) #define unpackH1H8(x) (((unsigned long long)((((x) >> 4) * 0x10204080) & 0x80808080) << 32) | ((((x) & 0x0f) * 0x10204080) & 0x80808080)) #endifだが確定石を求める用途では隅は横方向にも含まれているので、縦方向は A2-A7 と H2-H7 が求まればよく、6 ビットなら1回でできる。 (4.5.1)
#define unpackA2A7(x) ((((x) & 0x7e) * 0x0000040810204080) & 0x0001010101010100) #define unpackH2H7(x) ((((x) & 0x7e) * 0x0002040810204000) & 0x0080808080808000)また get_edge_stability で必要なのはビット数のみなので、unpack は省略できる。(ただし隅を重複して数えないように。) (4.5.0)
unsigned long long get_stable_edge(const unsigned long long P, const unsigned long long O)
{ // compute the exact stable edges (from precomputed tables)
return edge_stability[((unsigned int) P & 0xff) * 256 + ((unsigned int) O & 0xff)]
| (unsigned long long) edge_stability[(unsigned int) (P >> 56) * 256 + (unsigned int) (O >> 56)] << 56
| unpackA2A7(edge_stability[packA1A8(P) * 256 + packA1A8(O)])
| unpackH2H7(edge_stability[packH1H8(P) * 256 + packH1H8(O)]);
}
int get_edge_stability(const unsigned long long P, const unsigned long long O)
{
unsigned int packedstable = edge_stability[((unsigned int) P & 0xff) * 256 + ((unsigned int) O & 0xff)]
| edge_stability[(unsigned int) (P >> 56) * 256 + (unsigned int) (O >> 56)] << 8
| edge_stability[packA1A8(P) * 256 + packA1A8(O)] << 16
| edge_stability[packH1H8(P) * 256 + packH1H8(O)] << 24;
return bit_count_32(packedstable & 0xffff7e7e);
}
score = aspiration_search(search, SCORE_MIN, SCORE_MAX/*alpha, beta*/, search->depth, score);もう1つは、探索順を決めるときに置換表内に過去の探索結果があった場合にそれを優先するようになっているが、 過去の探索の深さが今回より4以上浅かった場合には採用せず、通常通り予備的な探索により評価するというもの。
else if (move->x == hash_data->move[0] && hash_data->depth > sort_depth - 3) move->score = (1 << 29); else if (move->x == hash_data->move[1] && hash_data->depth > sort_depth - 3) move->score = (1 << 28);いずれもコードの変更はごくわずかだが、勝敗読みには有効で、筆者の探索に対する理解の確かさを感じさせる。
Edax AVX のメインブランチでは 4.5.2 でこれらの変更を導入しているが、4.5 以降では探索ノード数 (fingerprint) が変化する変更が含まれるため、 Othello is Solved の探索数と同じになるように探索ノード数に影響しない最適化だけをバックポートしたブランチ 4.4.9mod2† も用意した。